In today’s digital landscape, the rapid growth of connected devices, IoT (Internet of Things), and real-time applications has transformed the way data is generated, processed, and utilized. Traditional cloud computing, while powerful, often struggles to meet the demands for speed, security, and efficiency required by modern applications. This is where edge computing emerges as a game-changing technology, revolutionizing data processing by bringing computation closer to the data source. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what edge computing is, its history, how it works, its benefits, challenges, and its role in shaping the future of technology.
Table of Contents
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data near the edge of the network, where data is generated, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers. Instead of transmitting all raw data to a remote cloud or data center for processing, edge computing enables local devices or servers—such as IoT sensors, gateways, or edge servers—to analyze and act on data immediately.
In simple terms:
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, reducing latency, bandwidth, and improving response times.
This localized processing is crucial for applications that require real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, smart cities, and healthcare devices.
A Brief History of Edge Computing
The concept of processing data at or near the data source isn’t entirely new. Its roots can be traced back to the early days of distributed computing and content delivery networks (CDNs). However, the modern era of edge computing began to take shape with the explosive growth of IoT devices in the 2010s.
Key milestones include:
- Early 2000s: Distributed computing architectures and CDNs aimed to optimize content delivery and reduce latency.
- 2010s: The proliferation of IoT devices, from smart thermostats to industrial sensors, created a need for local data processing.
- 2018-2020: Major tech companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Cisco began investing heavily in edge computing solutions, recognizing its potential to complement cloud computing.
- 2024: Edge computing has become a core component of digital transformation strategies across industries, especially for applications demanding ultra-low latency and high security.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
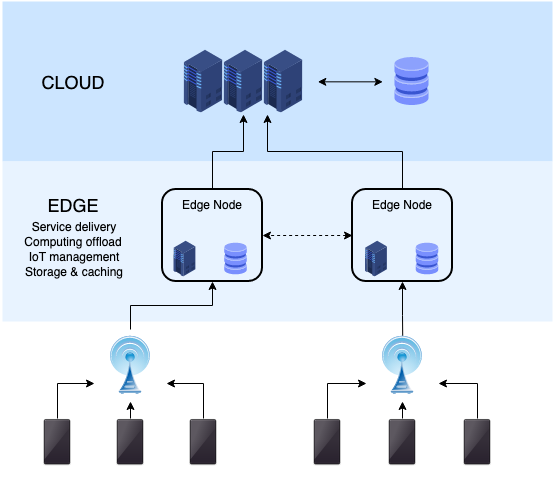
Edge computing involves a layered architecture that includes devices, edge nodes, and the cloud. Here’s a simplified overview:
- Data Generation: Devices such as sensors, cameras, and smartphones generate vast amounts of data continuously.
- Edge Nodes/Devices: These are local processing units—edge servers, gateways, or even smart devices—that analyze data in real-time. They filter, aggregate, or preprocess data before sending only relevant information to the cloud.
- Central Cloud or Data Center: For tasks requiring extensive computation, storage, or data aggregation, processed data or summaries are sent to centralized cloud platforms for further analysis, storage, or machine learning model updates.
Workflow example:
A smart security camera captures video footage. Instead of streaming hours of raw footage to the cloud, the camera’s onboard or nearby edge server detects motion, flags suspicious activity, and only transmits relevant clips or alerts, reducing bandwidth and response time.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Implementing edge computing offers numerous advantages:
1. Reduced Latency
By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes delays, enabling real-time decision-making critical for autonomous vehicles, industrial robots, and healthcare devices.
2. Bandwidth Savings
Sending only essential data to the cloud reduces network congestion and operational costs associated with data transmission.
3. Enhanced Privacy and Security
Processing sensitive data locally limits exposure, reducing the risk of breaches and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
4. Reliability and Resilience
Edge devices can operate independently of network connectivity, ensuring continuous operation even during network outages—vital for critical infrastructure.
5. Scalability
As the number of connected devices grows exponentially, edge computing helps manage data load efficiently without overwhelming centralized cloud resources.
6. Cost Efficiency
Reducing data transfer and storage costs, along with the ability to utilize existing local infrastructure, makes edge computing cost-effective.
Use Cases and Industries Benefiting from Edge Computing
Edge computing’s versatility makes it applicable across various sectors:
- Smart Cities: Traffic management, waste management, and surveillance systems operate efficiently with real-time data processing at the edge.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring devices analyze data locally for immediate alerts, improving patient care.
- Manufacturing: Industrial IoT sensors monitor equipment health, predict failures, and optimize production lines with minimal latency.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars process sensor data locally to make split-second decisions, ensuring safety and reliability.
- Retail: Smart shelves and checkout systems leverage edge devices to provide a seamless shopping experience.
- Energy: Smart grids and renewable energy systems utilize edge nodes to optimize energy distribution and consumption.
Challenges and Limitations of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers significant benefits, it also faces certain challenges:
- Security Concerns: Distributed edge devices increase attack surfaces, requiring robust security protocols.
- Management Complexity: Deploying, updating, and maintaining a vast network of edge devices can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Data Consistency: Ensuring data synchronization and consistency across distributed nodes can be challenging.
- Hardware Limitations: Edge devices may have limited processing power and storage compared to centralized data centers.
- Integration with Cloud: Seamless integration between edge and cloud environments requires sophisticated orchestration and management tools.
The Future of Edge Computing
As technology continues to evolve, edge computing is poised to become an integral part of the digital ecosystem. Key trends shaping its future include:
- 5G Integration: Faster and more reliable connectivity will enable more sophisticated edge applications, including AR/VR and immersive experiences.
- AI at the Edge: Deployment of AI models directly on edge devices will empower instant insights and autonomous decision-making.
- Hybrid Cloud-Edge Architectures: Businesses will adopt flexible architectures that leverage both cloud scalability and edge responsiveness.
- Standardization and Security Protocols: Developing industry standards will facilitate interoperability and security across diverse devices and platforms.
- Edge-as-a-Service: Managed services for edge infrastructure will lower barriers to adoption, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Embracing the Edge Revolution
Edge computing represents a paradigm shift in how data is processed and utilized in our increasingly connected world. By decentralizing data analysis closer to the source, it addresses critical challenges of latency, bandwidth, privacy, and reliability, enabling innovative applications across industries.
Organizations that embrace edge computing today will be better positioned to innovate, improve operational efficiency, and deliver superior experiences to their customers. As the technology matures and integrates with emerging innovations like 5G and AI, edge computing will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of digital transformation.
Stay ahead of the curve by understanding and leveraging edge computing—your gateway to faster, smarter, and more secure digital solutions.
imgage: Wikipedia
Why ARM-Based Laptops Are Gaining Ground in 2025
A Quiet Revolution in Your Laptop In 2025, ARM-based laptops are no longer niche. Once associated mo…
What Is Quantum Computing? A Complete Guide to the Future of Technology
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, quantum computing stands out as one of the most revolut…
Edge Computing: The Future of Data Processing and Connectivity
In today’s digital landscape, the rapid growth of connected devices, IoT (Internet of Things), and r…


